Note
Go to the end to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via Binder
Collocating external data¶
Script will use py-eddy-tracker methods to upload external data (sea surface temperature, SST) in a common structure with altimetry.
Figures higlights the different steps.
from datetime import datetime
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from py_eddy_tracker import data
from py_eddy_tracker.dataset.grid import RegularGridDataset
date = datetime(2016, 7, 7)
filename_alt = data.get_demo_path(
f"dt_blacksea_allsat_phy_l4_{date:%Y%m%d}_20200801.nc"
)
filename_sst = data.get_demo_path(
f"{date:%Y%m%d}000000-GOS-L4_GHRSST-SSTfnd-OISST_HR_REP-BLK-v02.0-fv01.0.nc"
)
var_name_sst = "analysed_sst"
extent = [27, 42, 40.5, 47]
Loading data¶
sst = RegularGridDataset(filename=filename_sst, x_name="lon", y_name="lat")
alti = RegularGridDataset(
data.get_demo_path(filename_alt), x_name="longitude", y_name="latitude"
)
# We can use `Grid` tools to interpolate ADT on the sst grid
sst.regrid(alti, "sla")
sst.add_uv("sla")
Functions to initiate figure axes
def start_axes(title, extent=extent):
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(13, 6), dpi=120)
ax = fig.add_axes([0.03, 0.05, 0.89, 0.91])
ax.set_xlim(extent[0], extent[1])
ax.set_ylim(extent[2], extent[3])
ax.set_title(title)
ax.set_aspect("equal")
return ax
def update_axes(ax, mappable=None, unit=""):
ax.grid()
if mappable:
cax = ax.figure.add_axes([0.93, 0.05, 0.01, 0.9], title=unit)
plt.colorbar(mappable, cax=cax)
ADT first display¶
![SLA, [m]](../../_images/sphx_glr_pet_SST_collocation_001.png)
SST first display¶
We can now plot SST from sst
![SST, [°K]](../../_images/sphx_glr_pet_SST_collocation_002.png)
![SST, [°K]](../../_images/sphx_glr_pet_SST_collocation_003.png)
Now, with eddy contours, and displaying SST anomaly
sst.bessel_high_filter("analysed_sst", 400)
Eddy detection
sst.bessel_high_filter("sla", 400)
# ADT filtered
ax = start_axes("SLA", extent=extent)
m = sst.display(ax, "sla", vmin=-0.1, vmax=0.1)
update_axes(ax, m, unit="[m]")
a, c = sst.eddy_identification("sla", "u", "v", date, 0.002)
![SLA, [m]](../../_images/sphx_glr_pet_SST_collocation_004.png)
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/py-eddy-tracker/conda/latest/lib/python3.10/site-packages/numpy-1.24.3-py3.10-linux-x86_64.egg/numpy/lib/function_base.py:4737: UserWarning: Warning: 'partition' will ignore the 'mask' of the MaskedArray.
arr.partition(
kwargs_a = dict(lw=2, label="Anticyclonic", ref=-10, color="b")
kwargs_c = dict(lw=2, label="Cyclonic", ref=-10, color="r")
ax = start_axes("SST anomaly")
m = sst.display(ax, "analysed_sst", vmin=-1, vmax=1)
a.display(ax, **kwargs_a), c.display(ax, **kwargs_c)
ax.legend()
update_axes(ax, m, unit="[°K]")
![SST anomaly, [°K]](../../_images/sphx_glr_pet_SST_collocation_005.png)
Example of post-processing¶
Get mean of sst anomaly_high in each internal contour
anom_a = a.interp_grid(sst, "analysed_sst", method="mean", intern=True)
anom_c = c.interp_grid(sst, "analysed_sst", method="mean", intern=True)
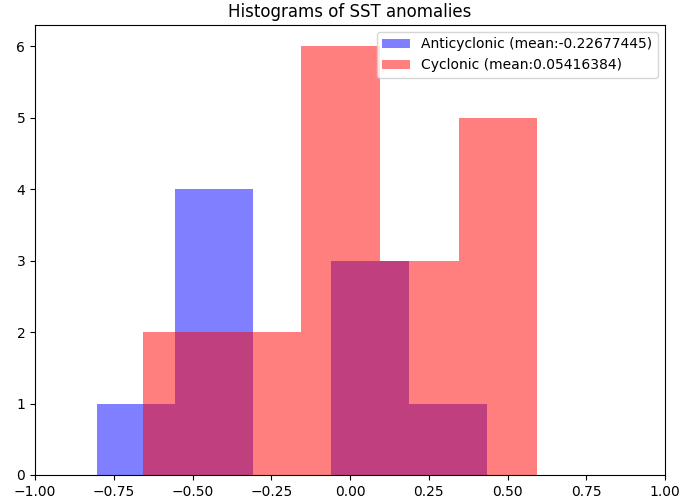
Are cyclonic (resp. anticyclonic) eddies generally associated with positive (resp. negative) SST anomaly ?
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(7, 5))
ax = fig.add_axes([0.05, 0.05, 0.90, 0.90])
ax.set_xlabel("SST anomaly")
ax.set_xlim([-1, 1])
ax.set_title("Histograms of SST anomalies")
ax.hist(
anom_a, 5, alpha=0.5, color="b", label="Anticyclonic (mean:%s)" % (anom_a.mean())
)
ax.hist(anom_c, 5, alpha=0.5, color="r", label="Cyclonic (mean:%s)" % (anom_c.mean()))
ax.legend()
<matplotlib.legend.Legend object at 0x7f2516583100>
Not clearly so in that case ..
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 9.373 seconds)